First of all, let’s see what are we going to achieve? Let’s say we have an dotnet 9 api application.
Its appsettings.json looks like:
"Color": "Color from appsettings",
"Person": {
"Name": "Name from appsettings"
}
Let’s try to retrieve these values:
app.MapGet("/", (IConfiguration config) =>
{
string color = config.GetSection("Color").Value ?? "No color";
string name = config.GetSection("Person:Name").Value ?? "No name";
return Results.Ok(new
{
color,
name,
message = "Hello there..."
});
});
If you visit this endpoint, you will see this output:
{
"color": "Color from appsettings",
"name": "Name from appsettings",
"message": "Hello there..."
}
Right now, these are just some dummy values. In reality, it can be connection strings, jwt secrets, secret to external services or any kind of secret. You don’t want to put these secrets in your application. You want to store them in a secret store or something. Key vault can be that store for you.
Let’s try to load these values from azure key vault.
Create a resource in azure portal
First and foremost you need to create a resource. Click on ‘+Create a resource’ and search Key vault
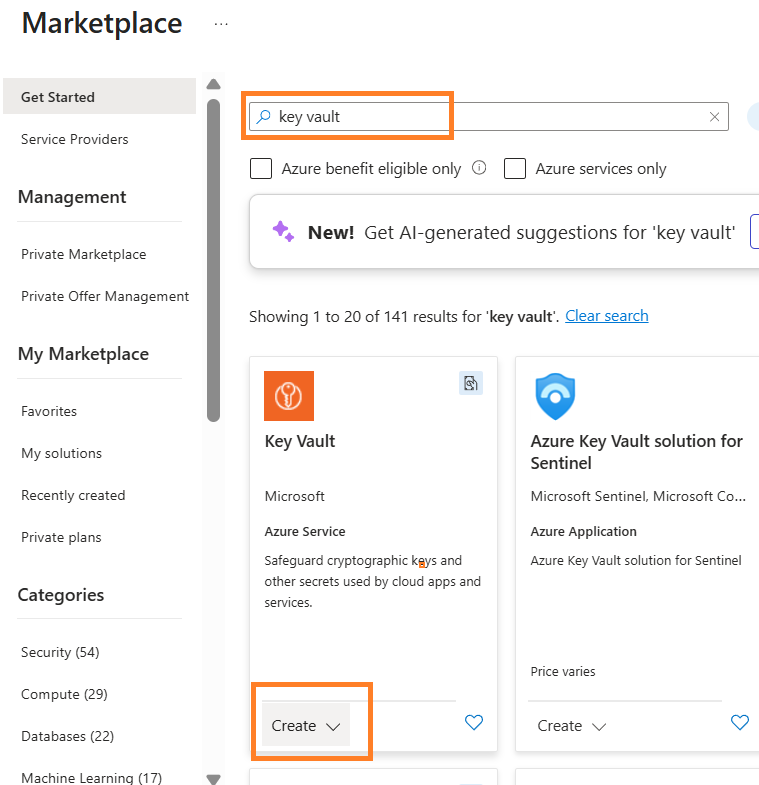
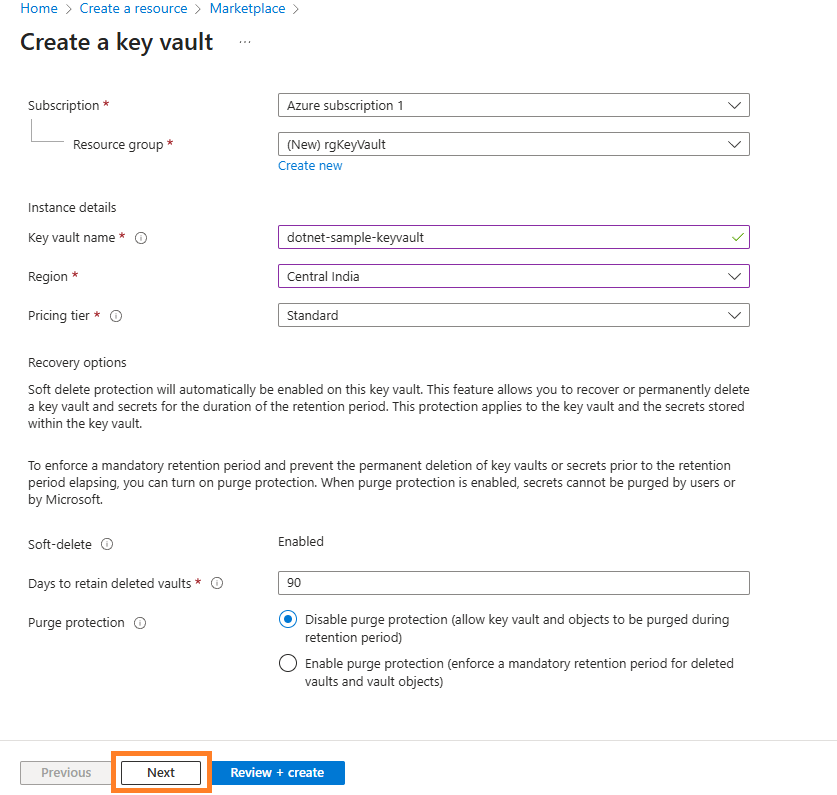
 Select
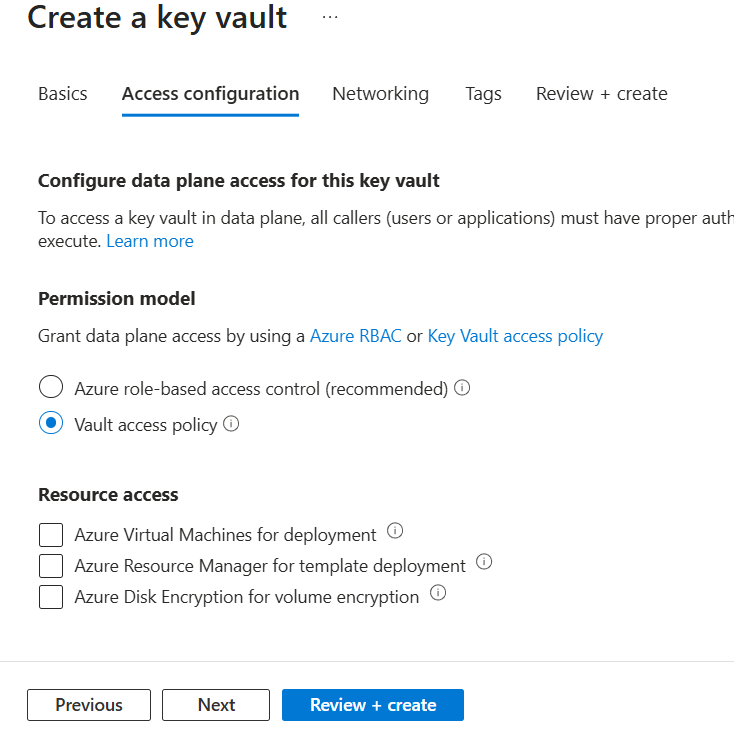
Select Vault access policy. However, Azure RBAC is recommended, but I find a bit difficult to use it.
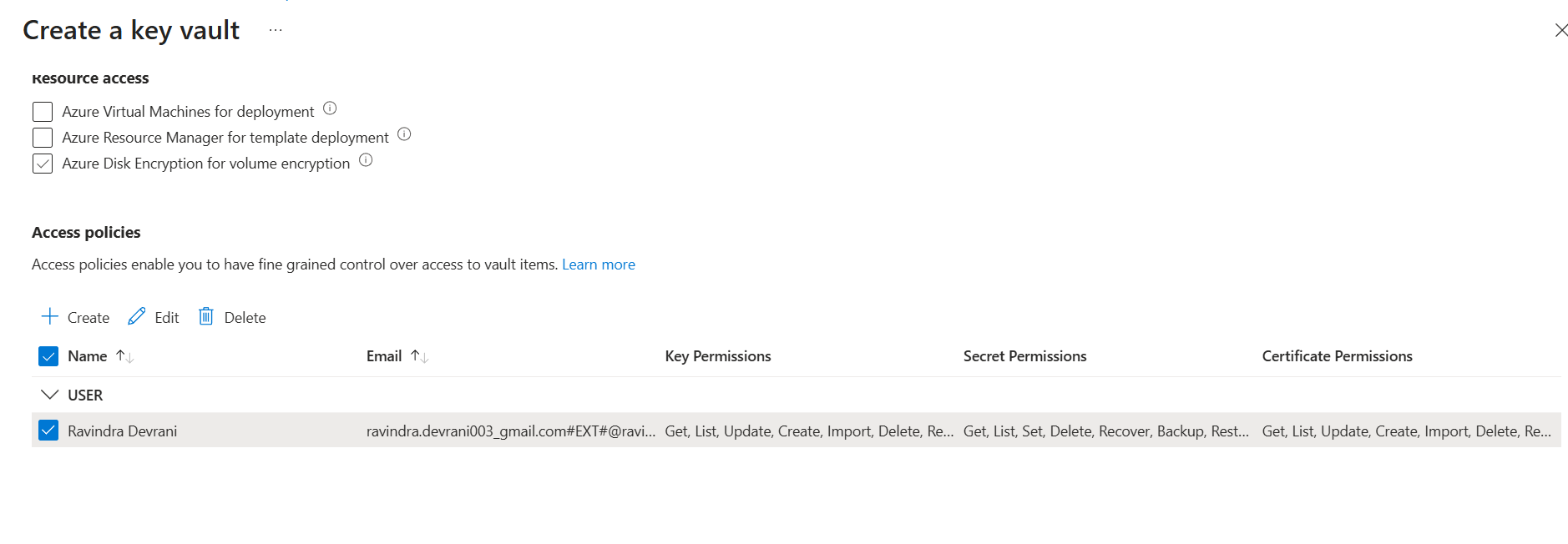
ravindra.devrani003_gmail.com#EXT#@ravindradevrani003gmail.onmicrosoft.com, is a user created in Entra Id.
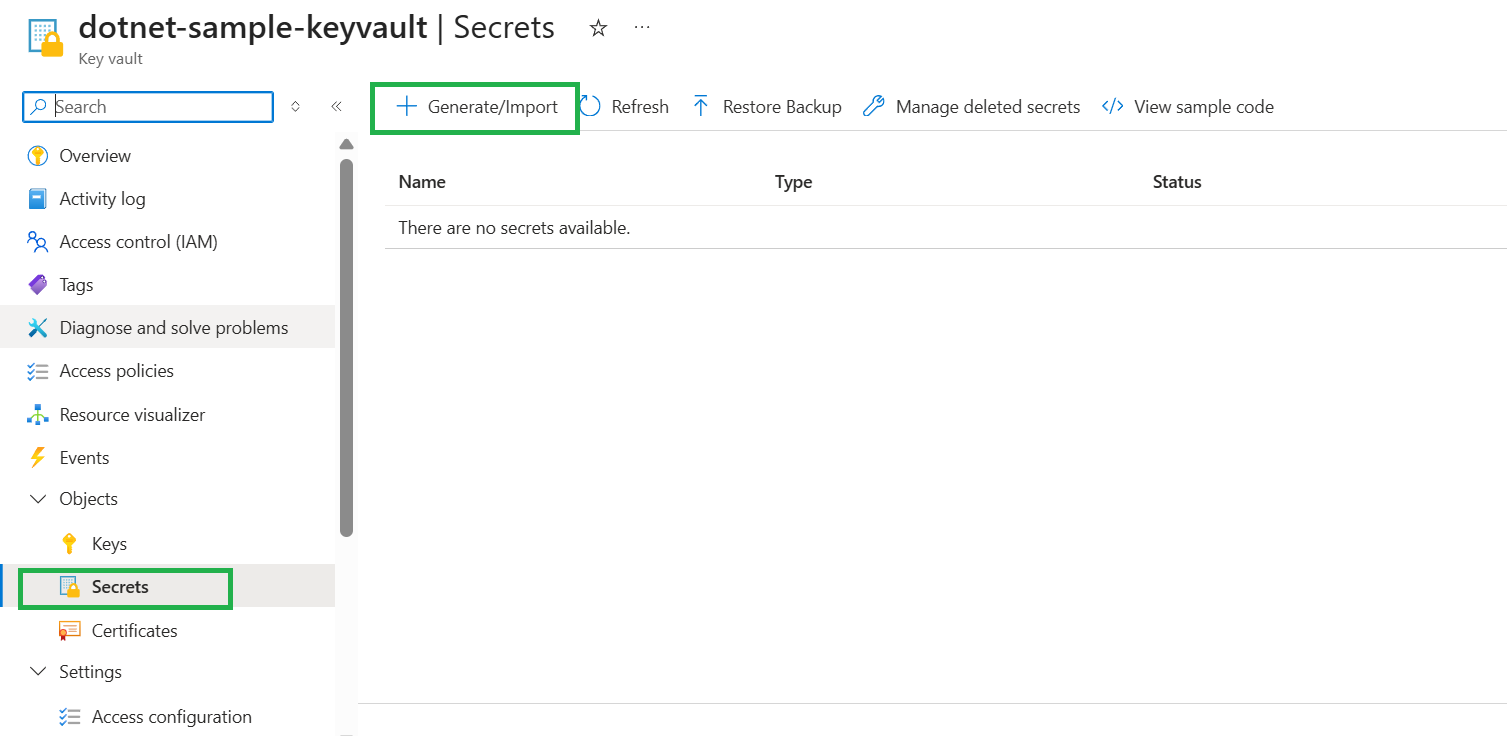
Secrets
Let’s add new secrets.
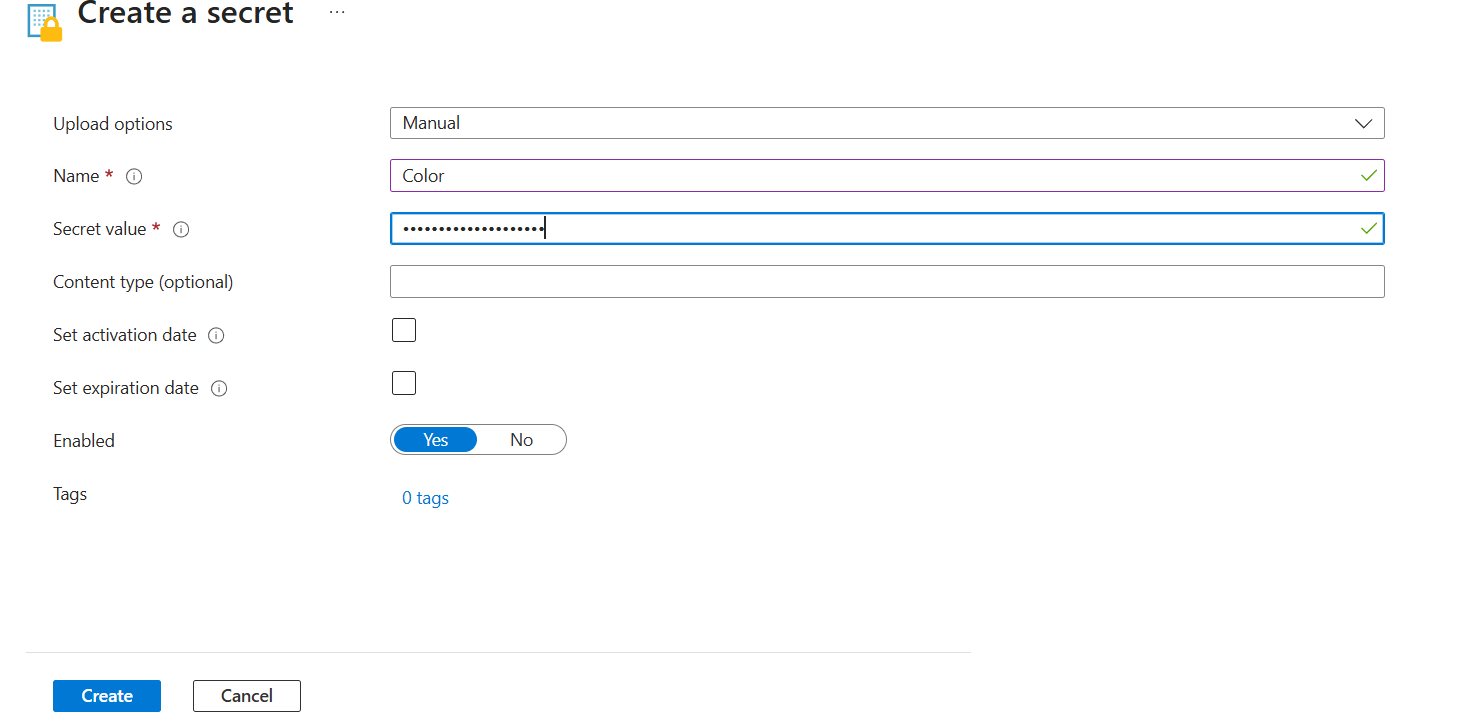
Let’s add another secret.
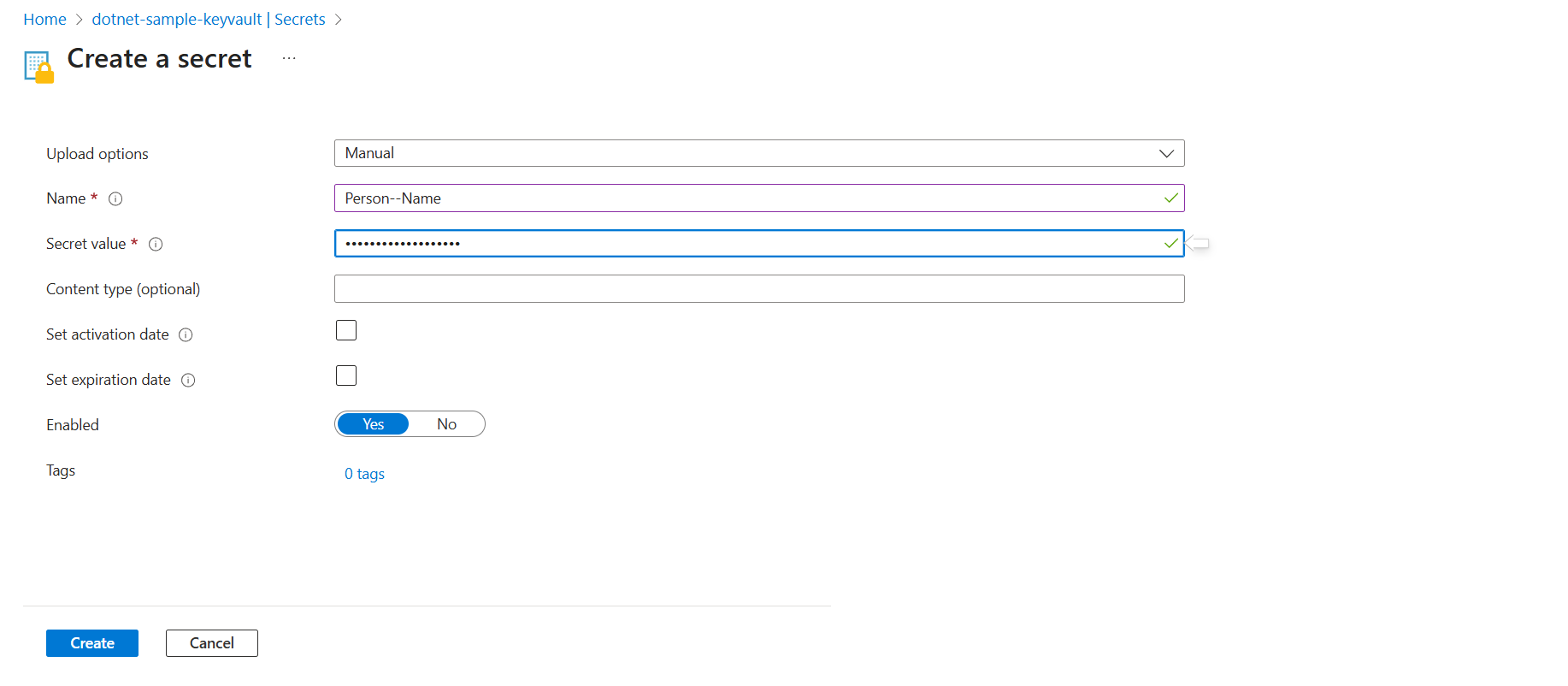
Person--Name will be mapped to Person:Name of dotnet app.
We are not going to store a connection string in the dotnet application, instead we are going to use Azure default credentials in our application. Make sure you have create an Entra Id user. With this user, you also need to log-in to visual studio (which will be shown later, just create a user for now).
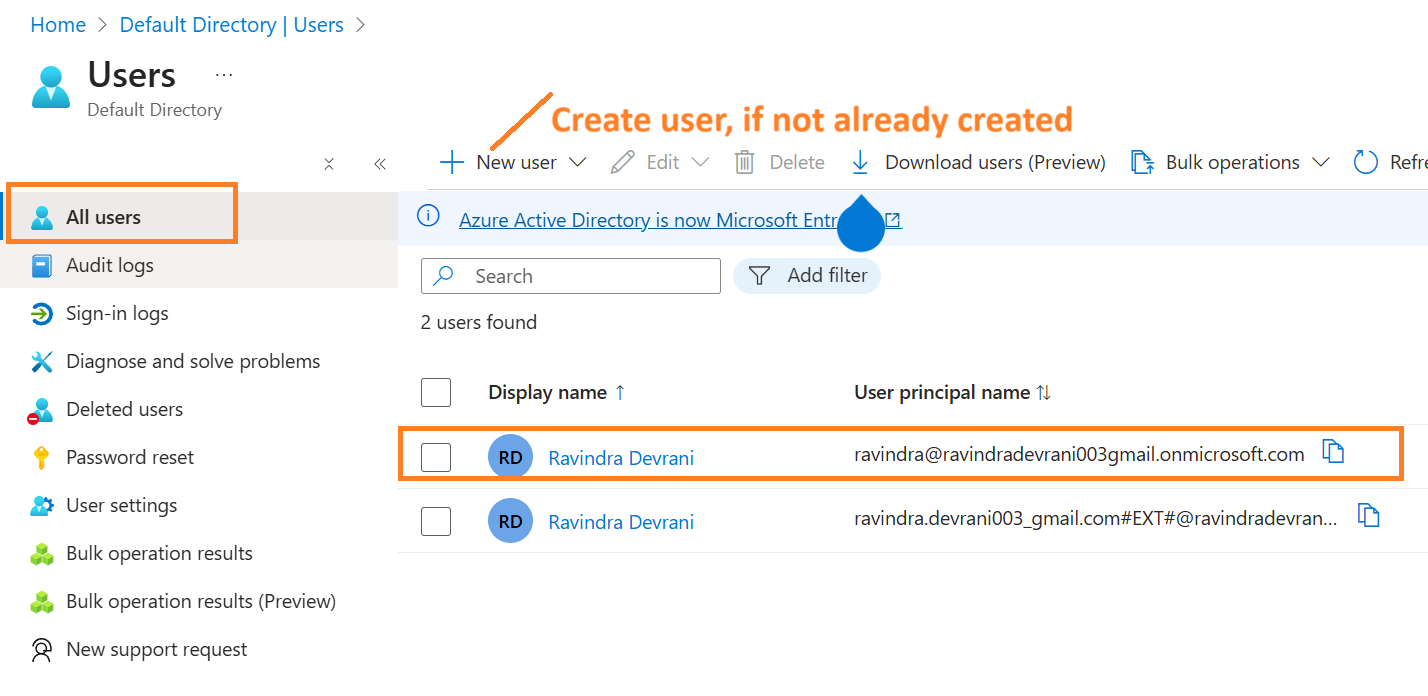
With the same user, you must need addtional login to Visual Studio.
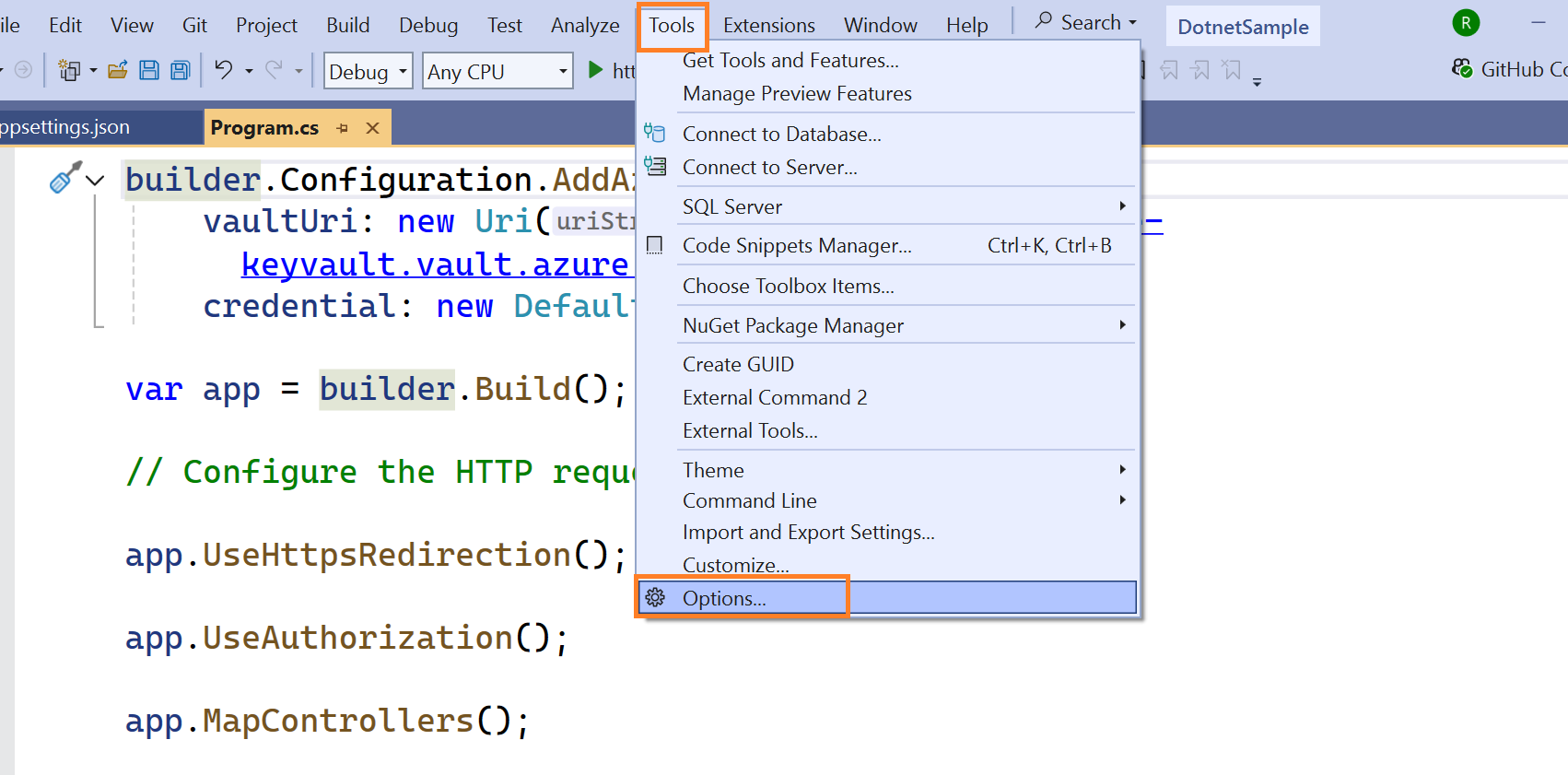
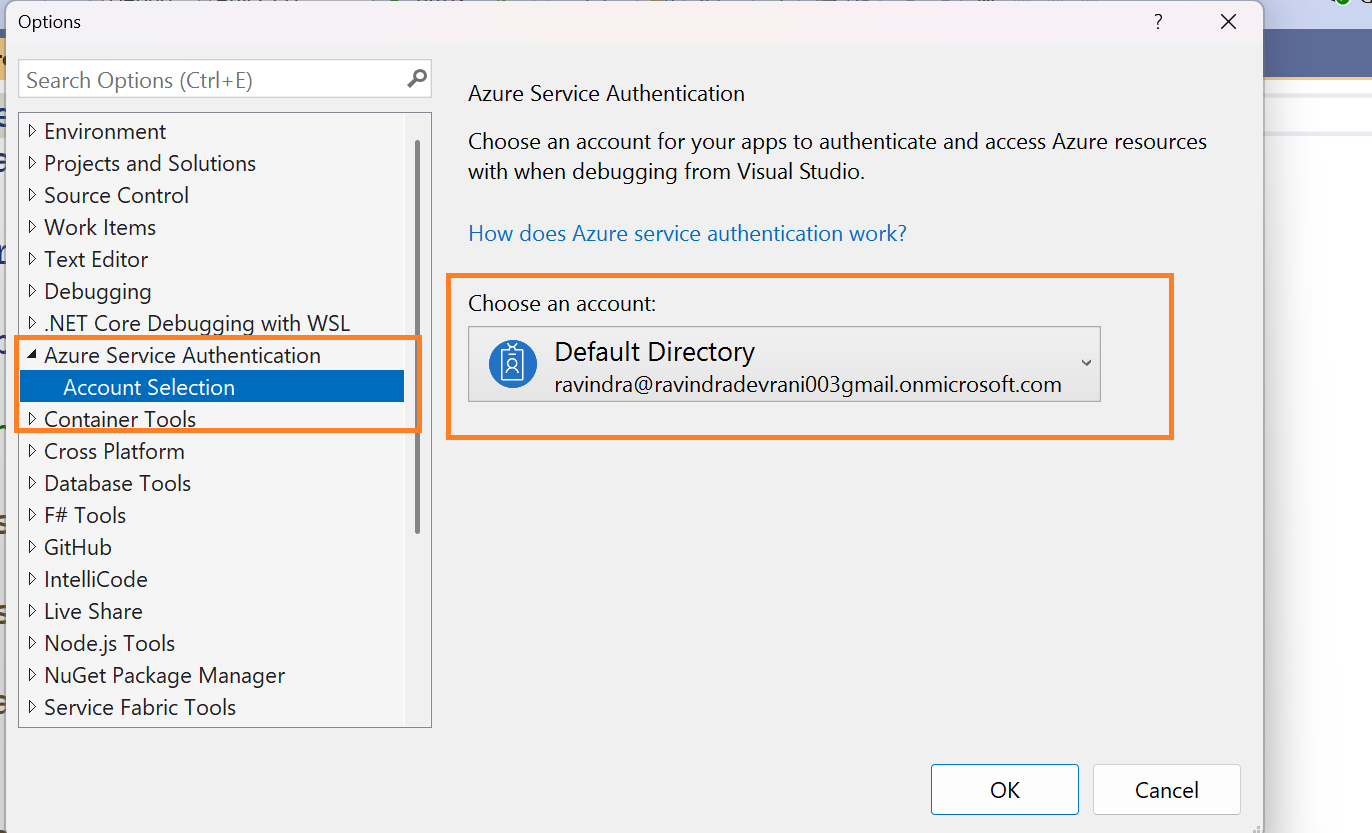
You also need to give permission to the same user.
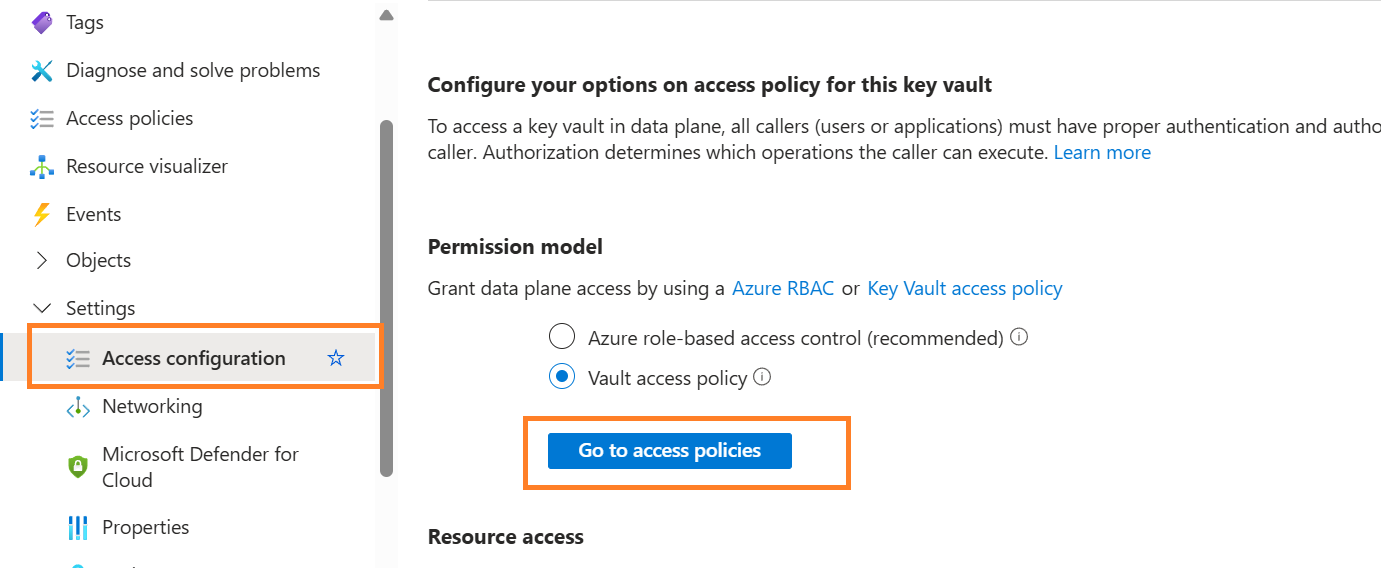
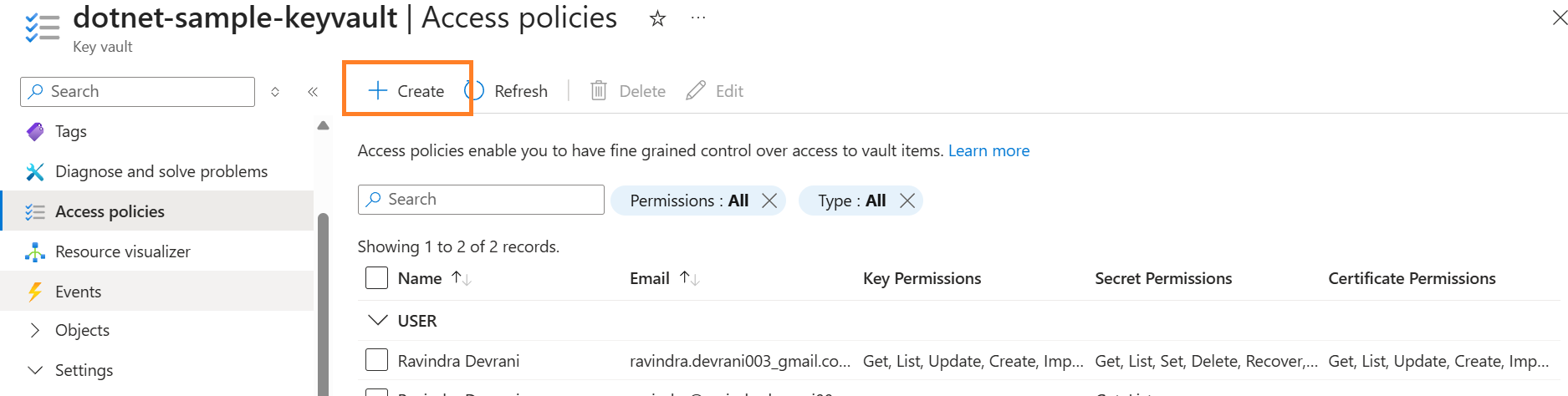
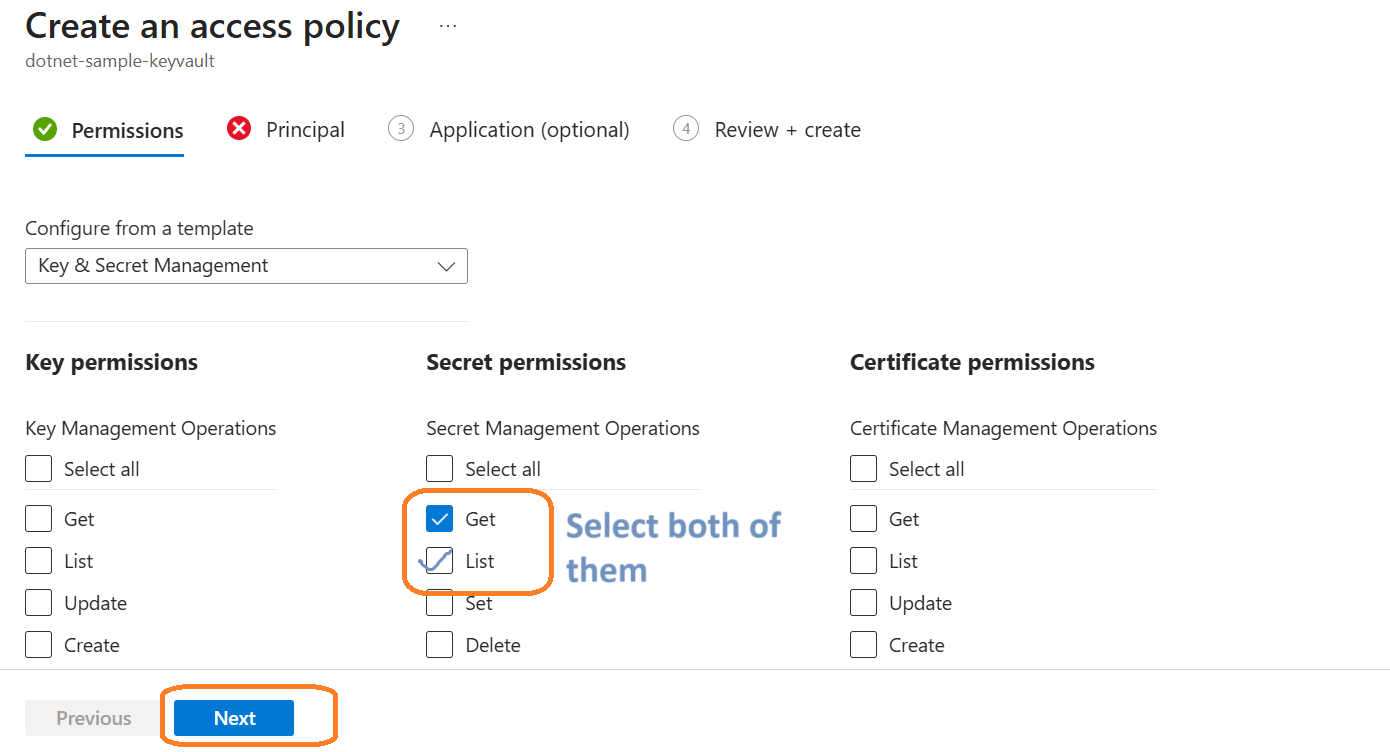
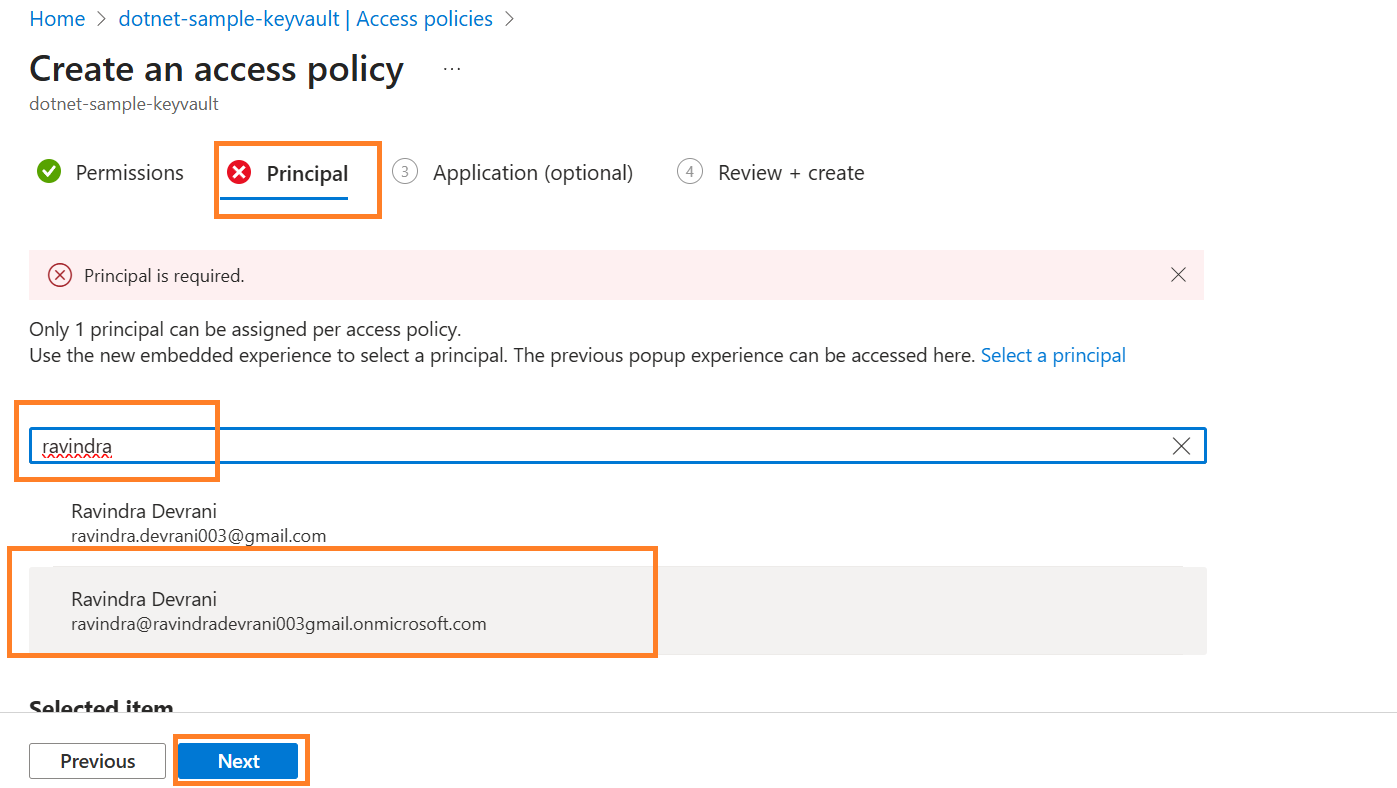
👉 Let’s move back to the visual studio.
Required nuget packages
Install-Package Azure.Identity
Install-Package Azure.Extensions.AspNetCore.Configuration.Secrets
Program.cs
builder.Configuration.AddAzureKeyVault(
vaultUri: new Uri("https://dotnet-sample-keyvault.vault.azure.net/"),
credential: new DefaultAzureCredential());
Or if you want to load these secrets only in production. That make more sense to me. Load configuration from appsettings in local and from key vault in production.
if (builder.Environment.IsProduction())
{
builder.Configuration.AddAzureKeyVault(
vaultUri: new Uri("https://dotnet-sample-keyvault.vault.azure.net/"),
credential: new DefaultAzureCredential());
}
If you run the application, your appsettings will be overriden by azure key vault.
{
"color": "Color from key vault",
"name": "Name from key vault",
"message": "Hello there..."
}
Azure key vault is not only limited to Secrets. You can also add Keys and Certificates.
Now we have seen what have we achieved with azure key vault. We can say:
📃 Azure Key Vault is a service, that securely stores and manages cryptographic keys, secrets and certificates.
