In this tutorial, we are going to make dotnet core web api application and perform all the CRUD (create, read, update and delete). I have tried to keep it simple and avoided any complexities like repository pattern.
Tech and tools used
- Dotnet 10
- MySql 8+ (in docker container. Click here, if you want to create a MySql container in docker)
- Entity Framework Core (ORM)
- .NET CLI and VS Code (alternate Visual Studio 2025)
Creating a project
Execute these commands in a sequence.
dotnet new sln -o MySqlEfCore
cd MySqlEfCore/
dotnet new webapi --use-controllers -n MySqlEfCore.Api
dotnet sln add MySqlEfCore.Api/MySqlEfCore.Api.csproj
# execute this if you want to open it in a vs code.
code .
Installing required packages
In .NET CLI
#First visit to the directory where cproj file is located
cd ./MySqlEfCore.Api/
dotnet add package MySql.EntityFrameworkCore --version 9.0.9
#for working with migrations
dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design --version 9.0.9
In Visual Studio (Package manager console):
Install-Package MySql.EntityFrameworkCore -Version 9.0.9
#for working with migrations
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools -Version 9.0.9
📢 As of 26-Dec-2025, MySql.EntityFrameworkCore is not available for EF Core 10. That is why I have to install Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools or Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design for EF Core 9.
Models
Create a folder named Models in MySqlEfCore.Api directory. Then create a class named Person in that folder.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace MySqlEfCore.Api.Models;
public class Person
{
public int Id { get; set; }
[Required]
[MaxLength(30)]
public string FirstName { get; set; } = null!;
[Required]
[MaxLength(30)]
public string LastName { get; set; } = null!;
}
It is called Domain or Entity class and represents a database table. Which means there will be a table named People(it is name defined it db set, which we will define later) with columns Id, FirstName and LastName.
Idis a primary key and it’s value is auto generated, usually starts from 1 and will increment by 1. By convention, EF Core makes Id, ID, TableNameId(PersonId in our case) an auto-generated auto-incremented primary key.FirstNameandLastNamewill benvarchar(30) not null
Database context
Create a file named AppDbContext in Models directory.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace MySqlEfCore.Api.Models;
public class AppDbContext : DbContext
{
public AppDbContext(DbContextOptions<AppDbContext> options): base(options)
{
}
public DbSet<Person> People { get; set; }
}
AppDbContext inherits the DbContext class. Let’s understand the DbContext and DbSet
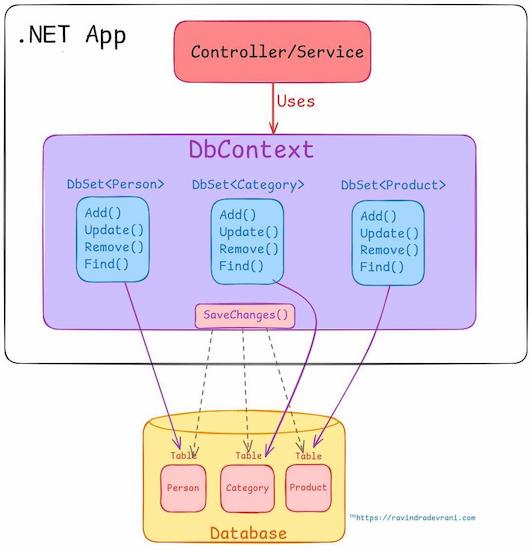
Database context: DbContext is a bridge between application’s entity classes and a database. It handles connection, queries data and persist changes to the database. It also provides change tracking. When you load data from the database, it is loaded in the session, you can change that data and save those changes to the databases.
DbSet: DbSet is a property that is mapped to a table in database.
Defining connection string
appsettings.json:
"ConnectionStrings": {
"default": "Server=localhost;Port=3306;database=PersonDb;Uid=root;Pwd=p@55w0rd"
}
Database PersonDb does not exists yet and will be created in migration section.
Registering Database context in a DI Container
Now, we need to register AppDbContext in DI Container, so we can inject it in our classes. Add these lines in Program.cs
string connection_string = builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("default") ?? throw new InvalidOperationException("Connection string not found");
builder.Services.AddDbContext<AppDbContext>(o => o.UseMySQL(connection_string));
Migrations
Make sure, you have installed ef core tools, if you are working with .NET CLI. To verify, execute dotnet ef command, which will draw a unicorn. If it is installed, make sure to update it to latest version with this command dotnet tool update --global dotnet-ef.
If it is not installed then execute the command given below:
dotnet tool install --global dotnet-ef
We need to follow two steps to make database changes.
- Create a migration file
- Update database
step 1: Create a migration file
For .NET CLI:
dotnet ef migrations add InitialCreate
For Visual studio(Package manager console):
Add-Migration InitialCreate
This step creates a migration file in Migrations folder. It contains the changes you are going to make in database.
Note that InitialCreate is the name of migration file and should be unique. It generates file with name like 20251226073326_InitialCreate (timestamp_fileNameGivenInMigrationCommand).
Always cross check the migration file to make sure it is what you want to do.
Step 2: Update database
Right now, we don’t have any database. Next command will create a database and tables or any updates you want to make in database.
dotnet ef database update
For Visual Studio (Package manager console):
Update-Database
It is a step which troubles most. If your connection string is not right, then you are going to see some error messages.
At this moment :
- Database
PersonDbis created. - Table
Peopleis created - Table
__MigrationHistoryis created. Which has two columns :- MigrationId : Whose value is
20251226073326_InitialCreatename of migration file` - ProductVersion:
9.0.1which is version of Entity Framework Core.
- MigrationId : Whose value is
Note that, You need to apply these two steps every time when you make a database change.
DTOs
DTOs are data transfer objects. They are just for transferring data between client and server. Client always not need to know all the columns of a table. For example, you have a User table which contains password field, you want to exclude that field for a client. In that case, we creates a dto class that does not contain password field. One more example, when you create a resource, you don’t need to provide Id, so we create a dto class named PersonCreate that excludes Id field.
Create a folder named DTOs in MySqlEfCore.Api. Create these DTOs in DTOs folder.
PersonCreate:
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace MySqlEfCore.Api.DTOs;
public class PersonCreate
{
[Required]
[MaxLength(30)]
public string FirstName { get; set; } = null!;
[Required]
[MaxLength(30)]
public string LastName { get; set; } = null!;
}
PersonUpdate:
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace MySqlEfCore.Api.DTOs;
public class PersonUpdate
{
public int Id { get; set; }
[Required]
[MaxLength(30)]
public string FirstName { get; set; } = null!;
[Required]
[MaxLength(30)]
public string LastName { get; set; } = null!;
}
PersonRead:
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace MySqlEfCore.Api.DTOs;
public class PersonRead
{
public int Id { get; set; }
[Required]
[MaxLength(30)]
public string FirstName { get; set; } = null!;
[Required]
[MaxLength(30)]
public string LastName { get; set; } = null!;
}
Mappers
We also need to convert DTOs to domain/entity classes (which are directly mapped to db) and vice versa. We are going to create extension methods for that. You can aslo use libraries like Automapper or mapster instead.
Create a folder named Mappers and create a class named PersonMapper in that folder. Person mapper will be a static class.
namespace MySqlEfCore.Api.Mappers;
public static class PersonMapper
{
public static PersonRead ToPersonRead(this Person person)
{
return new PersonRead
{
Id = person.Id,
FirstName = person.FirstName,
LastName = person.LastName
};
}
public static Person ToPerson(this PersonCreate person)
{
return new Person
{
FirstName = person.FirstName,
LastName = person.LastName
};
}
public static Person ToPerson(this PersonUpdate person)
{
return new Person
{
Id = person.Id,
FirstName = person.FirstName,
LastName = person.LastName
};
}
}
Controller
Create an API controller named PeopleController in Controllers folder. It should look like this:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace MySqlEfCore.Api.Controllers;
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class PeopleController : ControllerBase
{
}
Inject AppDbContext through constructor injection.
public class PeopleController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly AppDbContext _context;
public PeopleController(AppDbContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
}
Now we will define our endpoints.
Read All (GET):
[HttpGet()]
public async Task<IActionResult> GetPeople()
{
try
{
var people = await _context.People.AsNoTracking().ToListAsync();
var peopleRead = people.Select(p => p.ToPersonRead()); // mapped to DTO
return Ok(peopleRead);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return StatusCode(StatusCodes.Status500InternalServerError, ex.Message);
}
}
Read one (GET):
[HttpGet("{id}", Name = "GetPerson")]
public async Task<IActionResult> GetPerson(int id)
{
try
{
var person = await _context.People.FindAsync(id);
// check for not found and return status code accordingly
if (person is null)
{
return NotFound($"Person with id: {id} does not found.");
}
return Ok(person.ToPersonRead());
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return StatusCode(StatusCodes.Status500InternalServerError, ex.Message);
}
}
Create (POST):
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> CreatePerson(PersonCreate personCreate)
{
try
{
var person = personCreate.ToPerson();
_context.People.Add(person);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return CreatedAtRoute("GetPerson", new { id = person.Id }, person.ToPersonRead()); // GetPerson is a Name property defined in GetPerson() method's HttpGet() Attribute
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return StatusCode(StatusCodes.Status500InternalServerError, ex.Message);
}
}
update (PUT):
[HttpPut("{id}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> UpdatePerson(int id, [FromBody] PersonUpdate personUpdate)
{
if (id != personUpdate.Id)
{
return BadRequest("Ids mismatch");
}
try
{
var isPersonExists = _context.People.AsNoTracking().Any(p => p.Id == id);
// check for not found and return status code accordingly
if (!isPersonExists)
{
return NotFound($"Person with id: {id} does not found.");
}
var person = personUpdate.ToPerson();
_context.People.Update(person);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return NoContent(); // returns 204 NoContent status code
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return StatusCode(StatusCodes.Status500InternalServerError, ex.Message);
}
}
Delete (DELETE):
[HttpDelete("{id}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> DeletePerson(int id)
{
try
{
var person = await _context.People.FindAsync(id);
// check for not found and return status code accordingly
if (person == null)
{
return NotFound($"Person with id: {id} does not found.");
}
_context.People.Remove(person);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return NoContent(); // returns 204 NoContent status code
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return StatusCode(StatusCodes.Status500InternalServerError, ex.Message);
}
}
Testing
To test API, I am going to use VS Code’s Rest Client, which is kind of built-in in Visual Studio. You can follow this step in both Vs Code and Visual Studio. Or you can use the testing client of your choice like postman, insomnia etc.
Create a file named person.http in MySqlEfCore.Api folder. Past the content in that file given below. Make sure to change the port accordingly.
@base_address = http://localhost:5004/api/people
GET {{base_address}}
###
GET {{base_address}}/1
###
POST {{base_address}}
Content-Type: application/json
{
"firstName": "Tim",
"lastName": "Storm"
}
###
PUT {{base_address}}/4
Content-Type: application/json
{
"id":4,
"firstName": "Sue",
"lastName": "Storm"
}
###
DELETE {{base_address}}/4
Run application with dotnet run and test the application. You will see a link Send Request above each Http Verb(GET, POST etc.). You need to click on that link to execute the API.
