There are some common practices one should take care of while designing REST APIs.
There is also a video version of this post.
1. Use descriptive names for resources
- ❌ /api/getAllBooks
- ❌ /api/retrieveBooks
- ❌ /api/manageBooks
- ❌ /api/process
- ✅ /api/books
2. Use nouns not verbs
- ❌ /api/mangage-books
- ✅ /api/books
3. Use plural nouns
| ❌ Singular Nouns | ✅ Plural Nouns |
|---|---|
| /api/book | /api/books |
| /api/movie | /api/movies |
| /api/person | /api/people |
| /api/customer | /api/customers |
4. Use hyphens (-) in url for better readabilty
- ❌ /api/useraccounts
- ✅ /api/user-accounts
5. Never use crud method names in url
| HttpMethod | ❌❌❌ | ✅✅✅ |
|---|---|---|
| GET | /api/books/GetAllBooks | /api/books |
| GET | /api/books/GetBookById/{id} | /api/books/{id} |
| POST | /api/books/CreateBook | /api/books |
| PUT | /api/books/UpdateBook/{id} | /api/books/{id} |
| DELETE | /api/books/DeleteBook/{id} | /api/books/{id} |
6. Use http method properly
| HttpMethod | Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GET | /api/books | Indicates a get resources |
| GET | /api/books/{id} | Indicates a get resource with id |
| POST | /api/books | Indicates creating a resource |
| PUT | /api/books/{id} | Indicates updating a resource |
| DELETE | /api/books/{id} | Indicates deleting a resource |
7. Use Http StatusCodes Correctly
These are the most commonly used status codes.
| StatusCodes | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 OK | Successful GET request |
| 201 Created | Successful POST request |
| 204 No Content | Successful but do not return a content, useful in put requests |
| 400 Bad Request | Invalid request or input |
| 401 Unauthorized | When an unauthorized user attempts to access a resource |
| 403 Forbidden | User is authenticated but has no access rights for a resource |
| 404 Not Found | Resources not found |
| 500 Internal Server Error | Server Side error |
8. Provide a complete feedback to the user
We are just returning the 201 created status code without body:
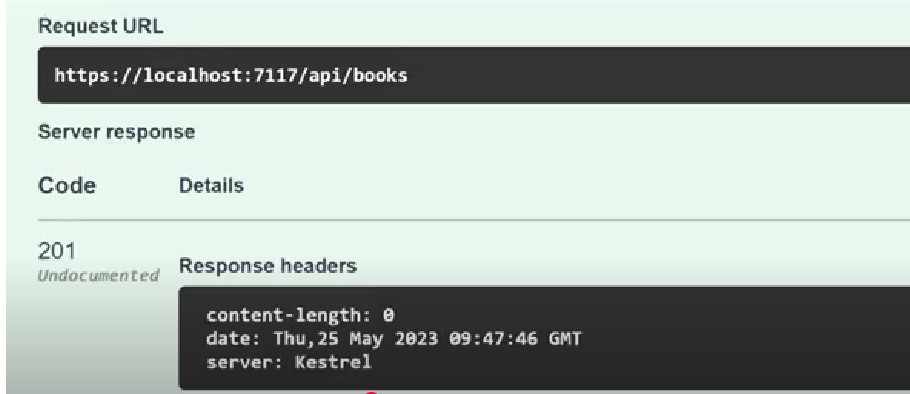
What if consumer needs a created resource. That is why we also need to return the created resource along with 201 status code.
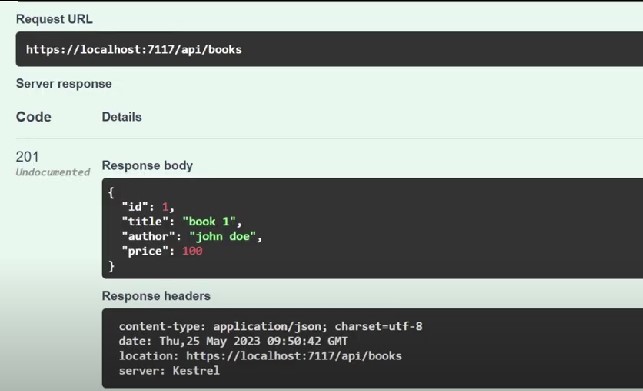
Now, it is up to the consumer whether one uses the created resource or not.
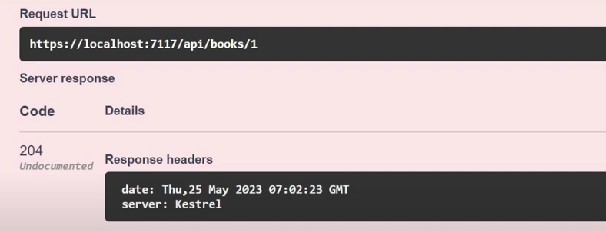
One more example
This one is absolute fine and widely practiced:
But this one is more descriptive:
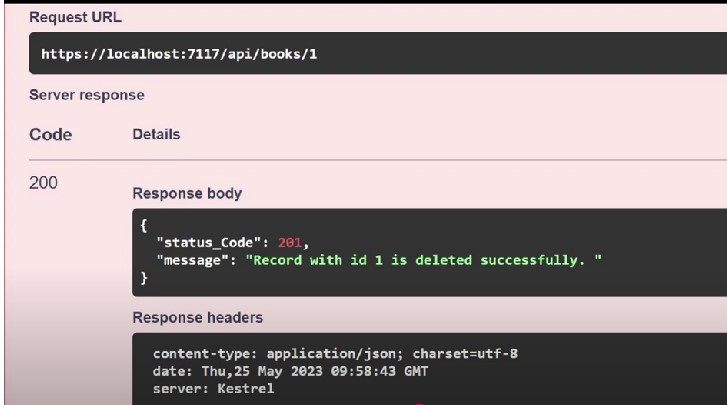
9. Use versioning
If you make some breaking changes in the API, it is better to create a new version of it, rather than breaking the existing API. In this way, a client application won’t break, and the clients makes changes whenever they need.
- version 1: /api/v1/books
- version 2: /api/v2/books
10. Use sub resources
Approach 1
- [GET]
/api/comments/{postId}(Comments for a specific post) - [GET]
/api/comments/{commentId}(Get a comment by commentId)
Approach 2
- [GET]
/api/posts/{postId}/comments(Comments for a specific post) - [GET]
/api/posts/{postId}/comments/{commentId}(Get a comment by commentId)
11. Always try to get detailed and meaningful error messages
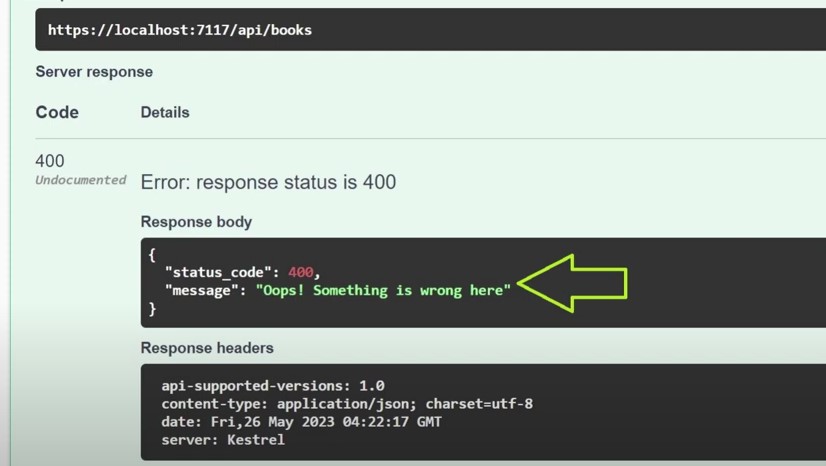
This one is a generic error. It does not clearly demonstrate the error.
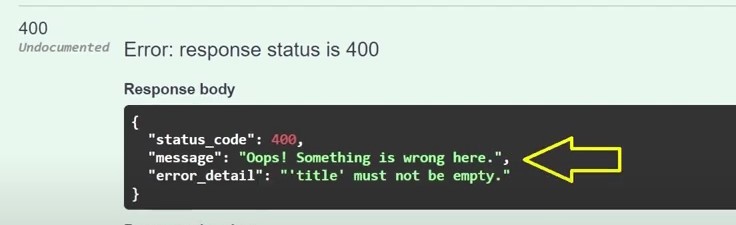
This one is more clear.
You can also use a modern approach by using Problem Details, which is introduced in rfc7807:
{
"type": "https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.4",
"title": "Resource not found",
"status": 404,
"detail": "User does not found",
"instance": "GET /api/greetings",
"traceId": "00-f4d3214afd423ad8d13d934062b283d7-f773987abae78043-00",
"requestId": "0HN8BHUP5M9SI:00000001"
}
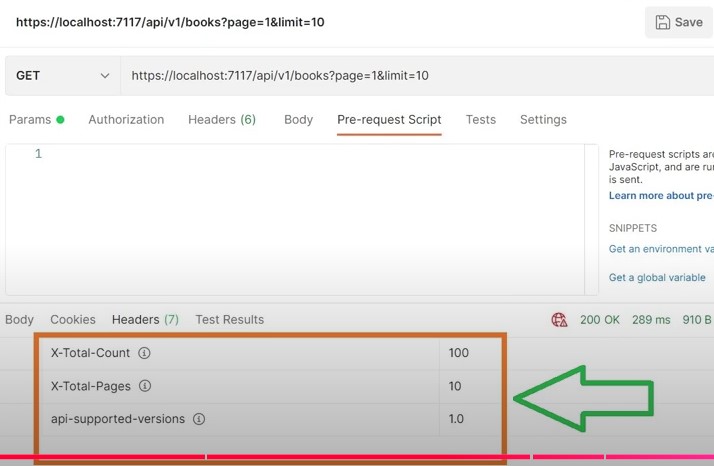
12. Implement pagination to limit the number of result
/api/v1/books?page=1&limit=10
You can pass additional information such as total-count, total-pages in the response header.
13. Use filters and sorting in apis
/api/v1/books?filter=pride(filter with title containing ‘pride’)/api/v1/books?sort=title(sort by title)/api/v1/books?sort=title desc(sort by title in descending order)/api/v1/books?filter=pride&sort=title desc(sort and filter both)
14. Use authentication in your apis
Use an authentication and role based access mechanism in your apis to protect it from an unauthorized access.
