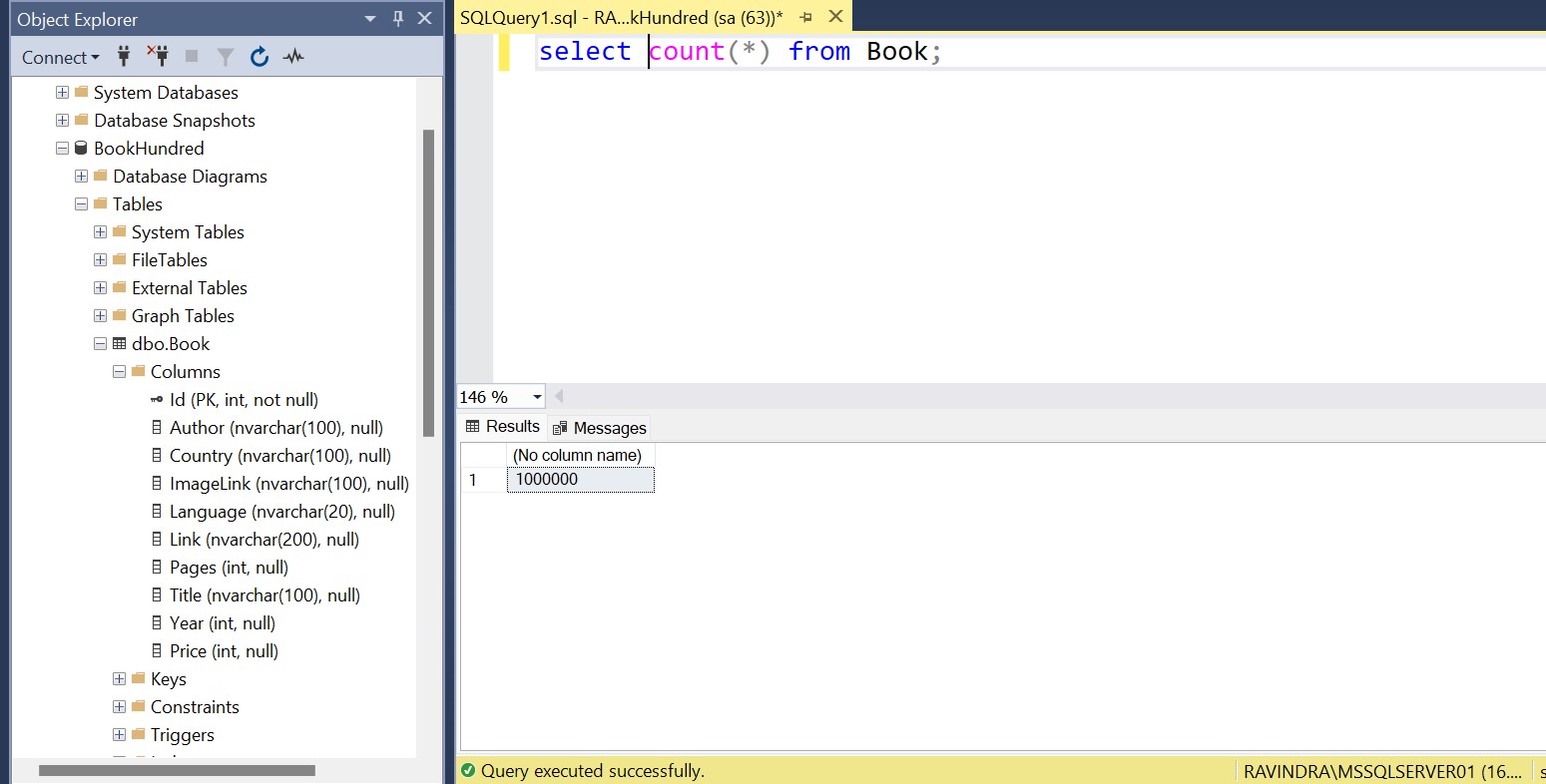
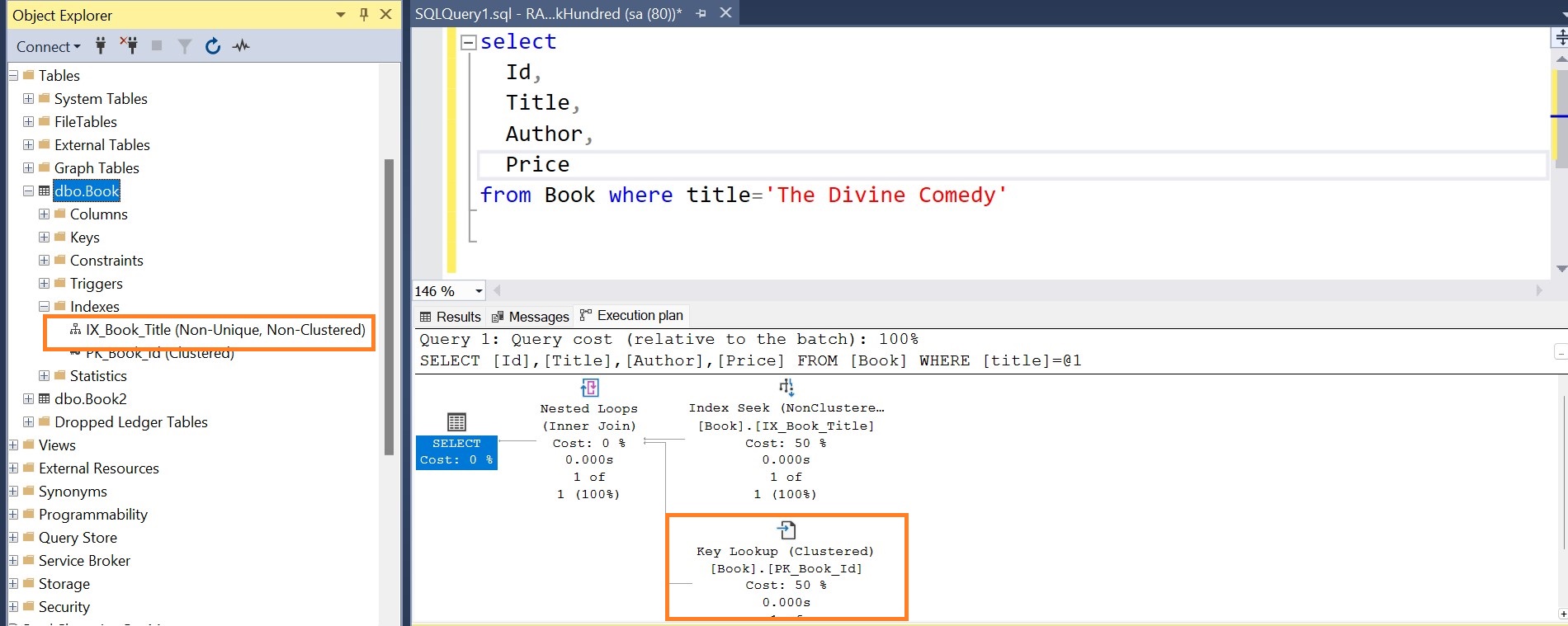
Stored procedure
CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE [dbo].[CreateTrackEntry]
@EntryDate DATE,
@SleptAt DATETIME2,
@WokeUpAt DATETIME2,
@NapInMinutes SMALLINT,
@TotalWorkInMinutes SMALLINT,
@Remarks NVARCHAR(1000) = NULL,
@TrackEntryId INT OUTPUT
AS
BEGIN
-- code removed for brevity
END
We have a stored procedure that returns TrackEntryId as an output parameter. Let’s see how can we execute it from the dapper?
using IDbConnection connection = new SqlConnection(_connectionString);
var parameters = new DynamicParameters(trackEntryToCreate);
// Input params
parameters.Add("@EntryDate", trackEntryToCreate.EntryDate);
parameters.Add("@SleptAt", trackEntryToCreate.SleptAt);
parameters.Add("@WokeUpAt", trackEntryToCreate.WokeUpAt);
parameters.Add("@NapInMinutes", trackEntryToCreate.NapInMinutes);
parameters.Add("@TotalWorkInMinutes", trackEntryToCreate.TotalWorkInMinutes);
parameters.Add("@Remarks", trackEntryToCreate.Remarks);
// output params
parameters.Add("@TrackEntryId", dbType: DbType.Int32, direction: ParameterDirection.Output);
await connection.ExecuteAsync("CreateTrackEntry", parameters,commandType:CommandType.StoredProcedure);
int trackEntryId = parameters.Get<int>("@TrackEntryId");